- The earth has two types of motions: rotation (घूर्णन) and revolution (परिक्रमण). Rotation is the movement of the earth on its axis. The movement of the earth around the sun in a fixed path or orbit is called Revolution.
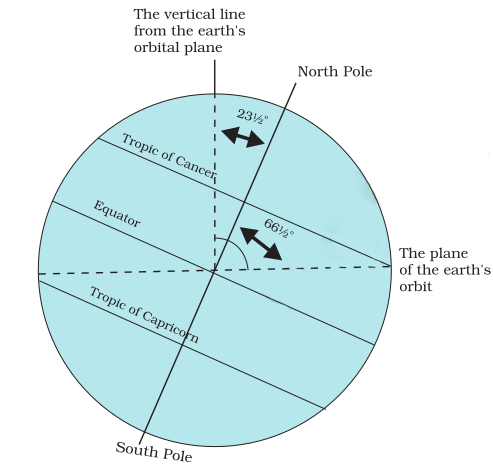
- The axis of the earth (an imaginary line),
makes an angle of 66½° with its orbital plane. The
plane formed by the orbit is known as the orbital plane.
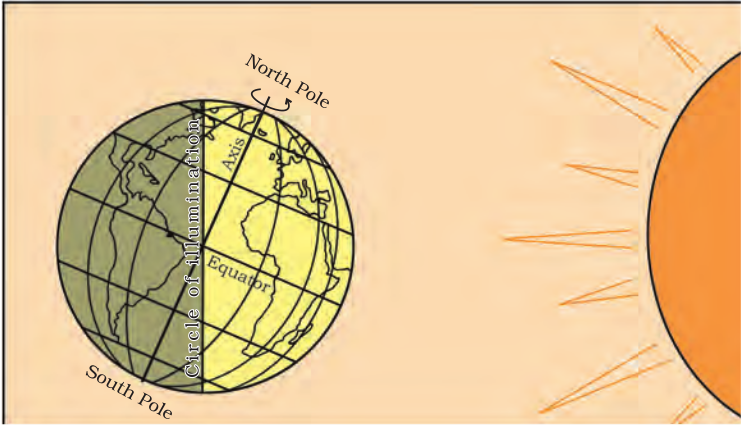
- The circle that divides the day from night on the globe is called the circle of illumination. This circle does not coincide with the axis.
- The earth receives light from the sun. Due to the spherical shape of the earth, only half of it gets light from the sun at a time. The portion facing the sun experiences day while the other half away from the sun experiences night.
- The earth takes about 24 hours to complete one rotation around its axis. The period of rotation is known as the earthday. This is the daily motion of the earth.
- Revolution takes 365¼ days (one year) to revolve around the sun. We generally consider a year as it consisting of 365 days and six hours saved every year are added to make one day (24 hours) over a span of four years. This surplus day is added to the month of February. Thus every fourth year, February is of 29 days instead of 28 days. Such a year with 366 days is called a leap year (अधिवर्ष).
- The earth is going around the sun in an elliptical orbit and throughout its orbit, the earth is inclined in the same direction.
Seasons of the Earth
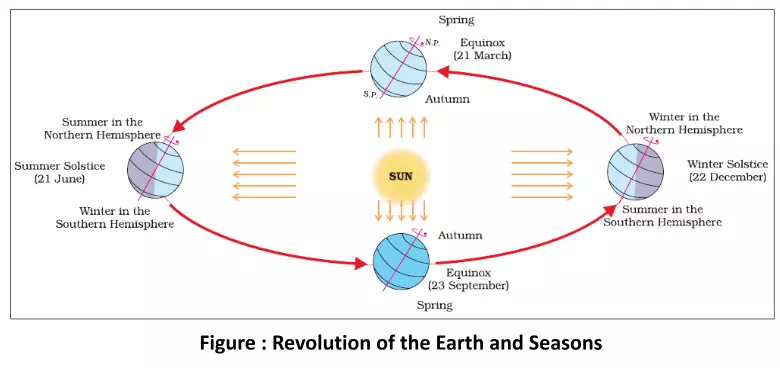
- A year is usually divided into summer, winter, spring, and autumn seasons. Seasons change due to the change in the position of the earth around the sun.
- On 21st June, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun. The sun rays fall directly on the Tropic of Cancer. As a result, these areas receive more heat. The areas near the poles receive less heat as the rays of the sun are slanting. The North Pole is inclined towards the sun and the places beyond the Arctic Circle experience continuous daylight for about six months. Since a large portion of the Northern Hemisphere is getting light from the sun, it is summer in the regions north of the equator. The longest day and the shortest night at these places occur on 21st June. At this time in the Southern Hemisphere all these conditions are reversed. It is winter season there. The nights are longer than the days. This position of the earth is called the Summer Solstice (उत्तरायण).
- On 22nd December, the Tropic of Capricorn directly receives the sun rays as the South Pole tilts towards it. As the sun’s rays fall vertically at the Tropic of Capricorn (23½° S), a larger portion of the Southern Hemisphere gets light. Therefore, it is summer in the Southern Hemisphere with longer days and shorter nights. The reverse happens in the Northern Hemisphere. This position of the earth is called the Winter Solstice (दक्षिणायन).
- On 21st March and 23rd September, direct rays of the sun fall on the equator. At this position, neither of the poles is tilted towards the sun; so, the whole earth experiences equal days and equal nights. This is called an Equinox (विषुव). On 23rd September, it is autumn season in the Northern Hemisphere and spring season in the Southern Hemisphere. The opposite is the case on 21st March, when it is spring in the Northern Hemisphere and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere.
Facts
- The ancient Indian astronomer Aryabhata have stated that ‘the earth is round and rotates on its own axis’.
- Due to the Winter Solstice, Christmas is celebrated in Australia in the summer season.
Comments
Post a Comment